The new MUSIQ Innovation newsletter on RAMAN SPECTROSCOPY: From applications to laser sources and detectors is available online and as a PDF . Each newsletter is written by three of MUSIQ’s Early Stage Researchers (ESRs) who choose their topics themselves to develop into an interesting read for our stakeholders. Our Innovation Newsletter n. 3 was written collaboratively by Jan Majer (ESR13), Dominykas Gudavičius (ESR15) and Ediz Herkert (ESR8).
Section n. 1
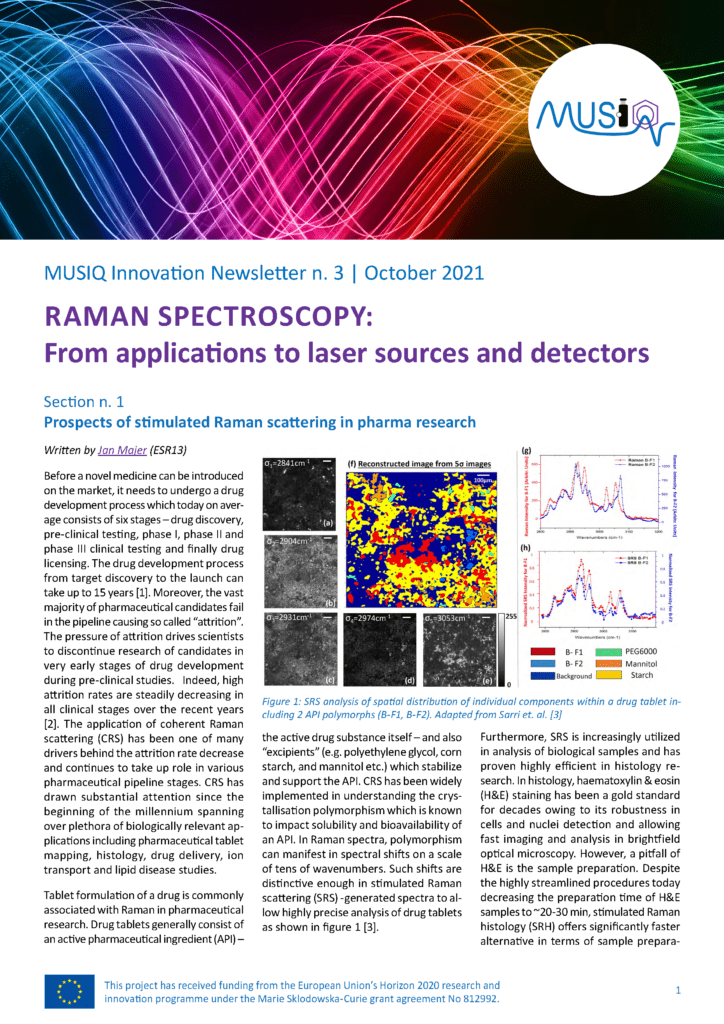
Prospects of stimulated Raman scattering in pharma research
Before a novel medicine can be introduced on the market, it needs to undergo a drug development process which today on average consists of six stages. The drug development process from target discovery to the launch can take up to 15 years. Read more
Section n. 2
Light sources for CARS microscopy
In coherent anti-Stokes Raman scattering (CARS) microscopy two laser beams are used to produce radiation at a third wavelength when energy difference between pulses matches vibrational energy of a sample. For this vibrationally specific microscopy method it is critical to have a reliable wavelength-tunable light source to address different Raman bands. Optical parametric amplifiers (OPAs) and oscillators (OPOs) are well suited for this task. Read more
Section n. 3
EMCCD and sCMOS cameras for scientific imaging
A comparison of the key figures of current camera models
The emergence of faster and more sensitive scientific cameras allows to acquire images with unprecedented sensitivity and speed. This is particularly important for applications in life sciences where techniques like Raman imaging require low-noise detectors while other techniques like fluorescent correlation spectroscopy rely on frame rates in the upper kilohertz range. To obtain meaningful data it is therefore essential to choose the scientific camera according to the experimental conditions. Read more

